Both Jean Piaget and Lev Semionovich Vigotsky , contributed in psychology to the study of cognitive development, related to the thinking and learning processes of people. Both belonged to the constructivist current , that is, they both affirmed that learning was the product of a mental construction.
Constructivists also consider that culture limits learning, since the beliefs of a person (who has been learning over time), as well as the influence of their society, select what the individual will end up learning and assuming.
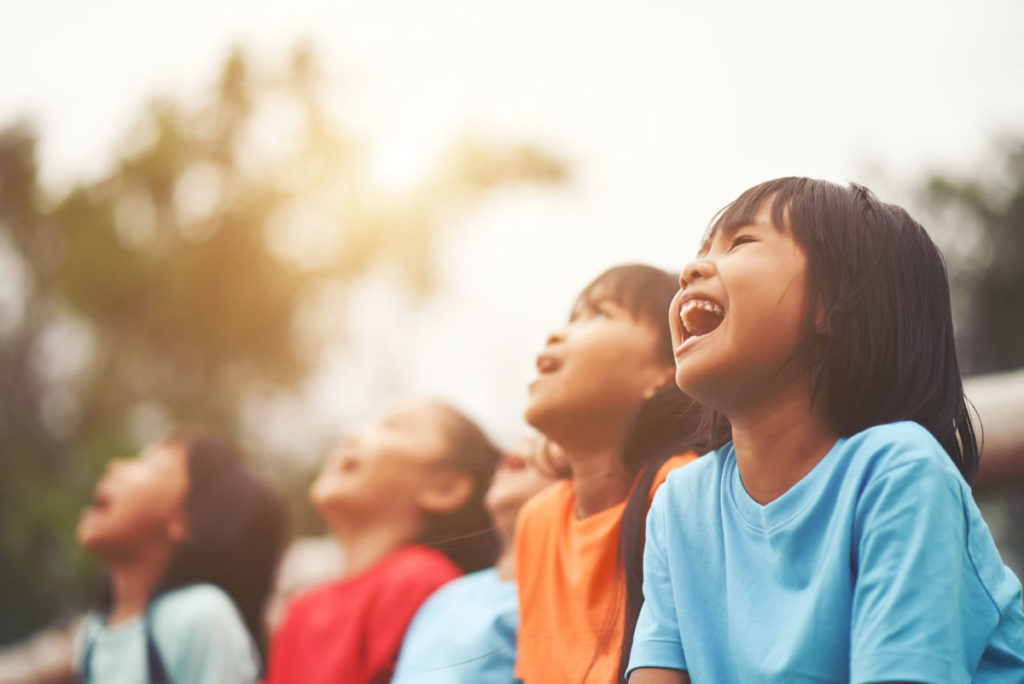

However, the differences between the two experts are possibly the greatest contribution to the contribution of learning in recent centuries . Let’s see what are the main differences between these two researchers regarding educational theories.
Comparison between Piaget and Vygotsky and their educational theories
- The importance of developmental stages in the learning process for Piaget
This is one of the main differences between the two characters. Piaget believed that development controls learning, and that people learn more or less depending on the stage of development in which they are. Piaget set 4 stages around this: sensorimotor stage (from birth to 2 years) in which the child learns thanks to physical activity; preoperational stage (2 to 7 years) in which language, memory and imagination develop; operational stage (from 7 to 11 years old) typical of logical thinking and in which one learns to do mental operations; and the last stage called the formal operational stage (from the age of 11) where the capacity for abstract thinking develops, a stage that not all people reach.
For his part, Vigotsky considered that learning is independent of the stage of development in which people are, or what is the same, that there are no pre-established stages for human learning.
- The importance of 3 elements in learning for Vygotsky
According to Vygotsky’s educational theory, there are moments in life of great development for learning, above the concrete stages, such as those formulated by Piaget. The first moment occurs in the intimate conversation for this researcher, when a child talks to himself looking for a solution, activates thought and thus stimulates learning. Another element that occurs at any time in life is being in the zone of proximal development, and by this Vygotsky meant that at any moment we find ourselves on the frontier of knowledge to go from not knowing to discovery. It is the moment when the child does not manage to develop any skills by himself but is close to achieving it. The role of the parent or educators at that time is to give advice or suggestions so that the child learns new concepts. Finally, there would be staggering, which is the time when the child is able to self-regulate to discover more and more with less help and dependence on others.
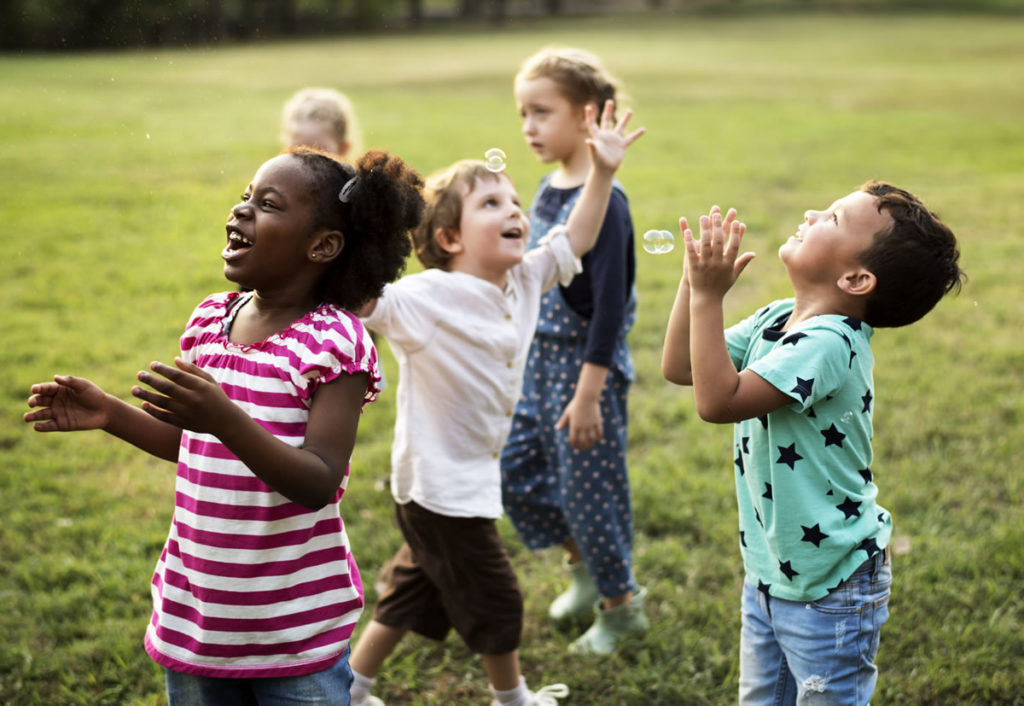

- The influence of the social environment on learning
Finally, one of the great differences between the two teachers should be highlighted, which was the thought they had about the influence of the social environment on children’s learning. For Piaget, the human being when he is born is a biological individual who learns socialization processes over time, but learning is built individually.
But to this Vygotsky responded in another way, since he believed that the child grows as a social individual promoting collaborative learning, since this is built by the organized perception that it creates in social interactions.
Knowing these characters so relevant to education and learning is vital for any teacher, as well as their respective contributions and differences in their way of analyzing and observing the learning and development of children. Despite the fact that some of their thoughts are outdated, they continue to be a reference in the education landscape and a fundamental part of the way in which educational systems are structured today and academic development is approached.
And you, whose are you more? Piaget or Vygotsky? Let us know in the comments!









































































































Excellent publication… I am more of Piaget